(Last Update 01-10-2024)
– Traditional Large Language Model (LLMs), although skilled in various tasks, do not possess the necessary specialization to offer effective mental health support. In response to the critical need for mental health support, particularly for individuals facing distressful situations and heightened risks to their well-being, and posting to various online support groups, the initiative aims to develop a specialized LLM.
–The objective is to develop an LLM program specifically designed to assist individuals facing mental health challenges. Designing a system that can analyze the patient's personality, the level of risk, and provide appropriate answers/comments is a significant challenge.
– Orchastreated a comprehensive step-by-step solution design. Performed intelligent prompt engineering with several SOTA LLMs (Llama2, GPT-3, Mistral-7b), supervised fine-tuning, and fine-tuning with Reinforcement Learning with Human and AI feedback.
– While the initiative is still in progress, early results show positive progress toward the creation of an LLM specifically designed for mental health support. The coordinated use of prompt engineering and fine-tuning approaches is resulting in a more complex understanding of users' mental states, allowing the model to provide intelligent and empathic replies.

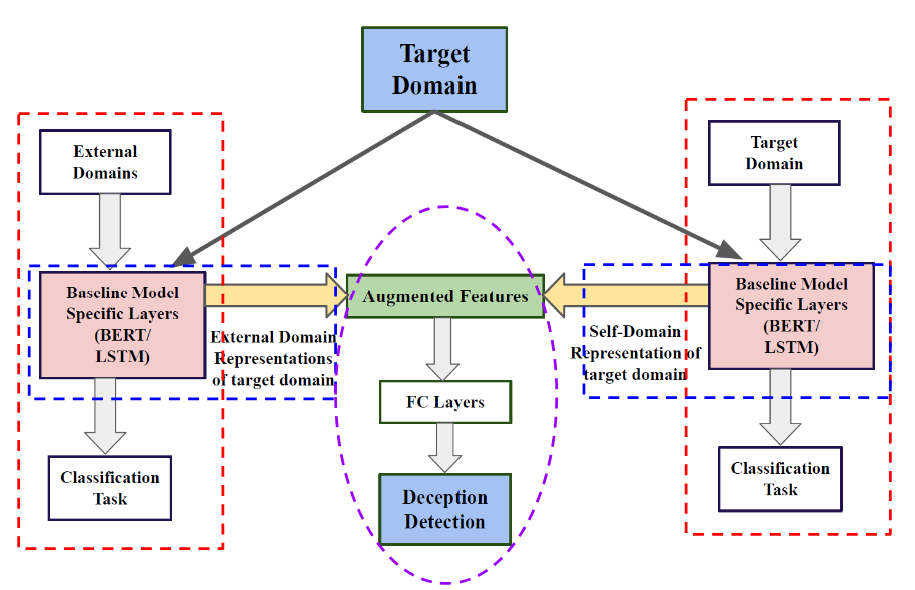
– The web being a fertile ground for deceptive text in different domains like Fake News, Phishing Emails, Fake Reviews, and Rumors, the SOTA detection methods are domain-specific, and as such, detection model in one domain doesnot work for the other. However, a major discrepancy in the data distribution in these domains requires a method of deceptive knowledge transfer.
– Conducted several in-depth ML-based analyses for a successful domain transfer that includes intermediate-layer concatenation, holistic training, and multi-task learning. Used cutting-edge techniques like BERT, character-level CNN, Sentence-BERT, and attention-based LSTM.
– Built a sophisticated domain-transfer technique, which was the first in the field, and improved performance over the self-domain training strategy by up to 18% in F1-score. Published results in three conferences: RANLP ’21, and ‘23, and SOCINFO’ 22.
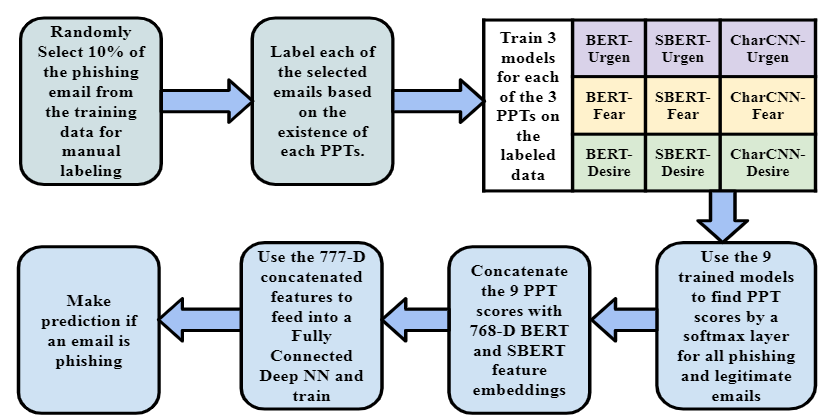
– Despite numerous attempts of phishing email detection, attackers are ever-evolving, often outsmarting the efforts. The project aimed to improve phishing email detection by detecting and utilizing unique psychological traits present in phishing emails.
– Identified and quantified three dominant psychological traits in phishing emails (PPT): A Sense of Urgency, Inducing Fear by Threatening, and Enticement with Desire, using BERT, Sentence-BERT, Character-level-CNN. Also employed GPT-2 for balanced training.
– Achieved a significant performance improvement of 4.54% in F1-score by using the PPT scores in phishing email detection over the SOTA approaches, with Fear being the most prominent PPT. Published result in WBC ‘22, and won the best paper award.
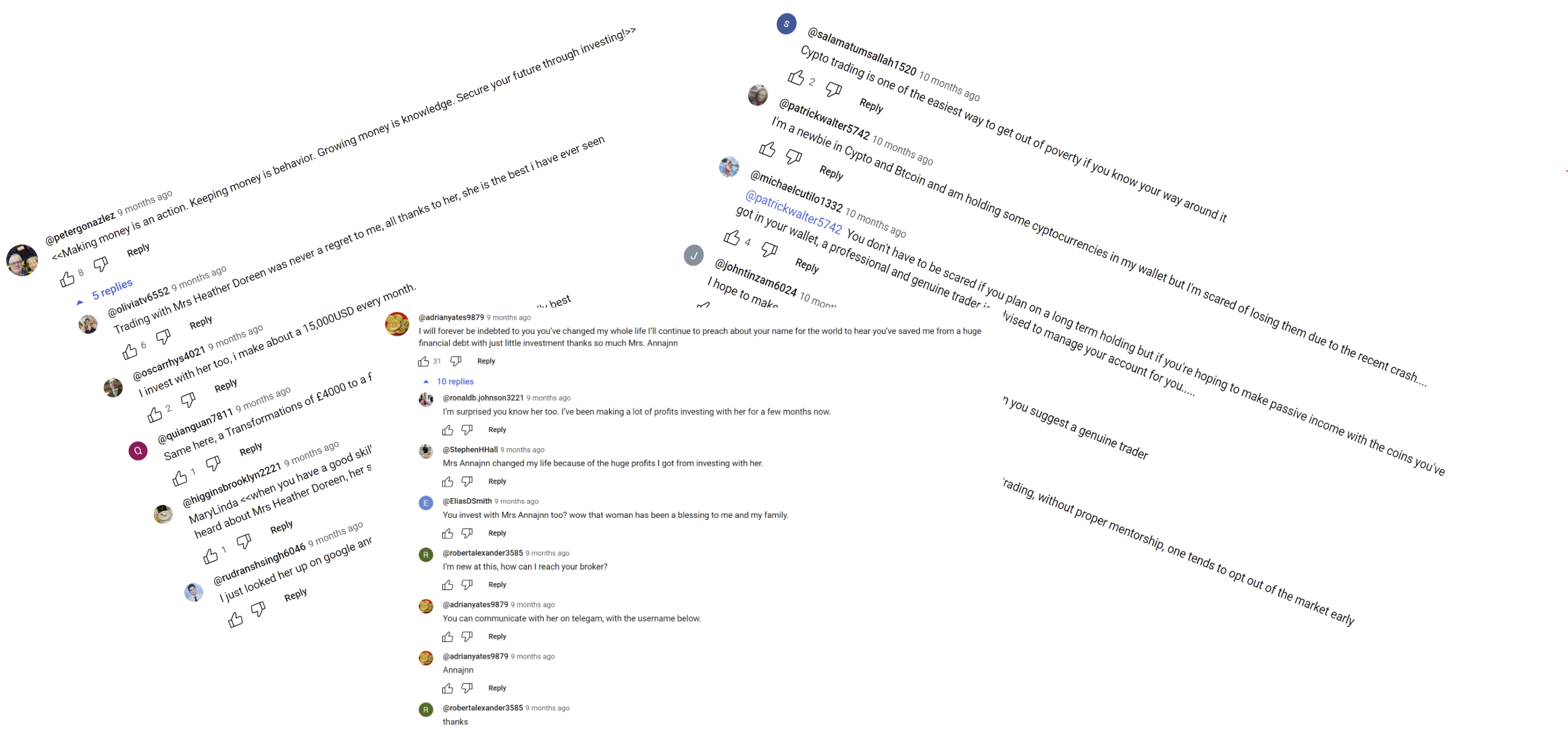
– The YouTube comment section has long been plagued by scammers, despite efforts to curb their activities, and now, a new type of scam, known as the "Collusion Scam," has emerged as a prominent threat within YouTube comments, particularly in the context of the cryptocurrency market.
– Performed data collection using YouTube API, and conducted analysis and detection of collusion scams using tf-idf, logistic regression, BERT, and zero-shot LLM training.
– Built the first dataset for collusion scam, developed deep learning techniques for successful collusion scam detection, and demonstrated the efficacy of leveraging metadata like the timespan, like count, and age of the channel in the detection process. Published one conference paper in RANLP ‘23.
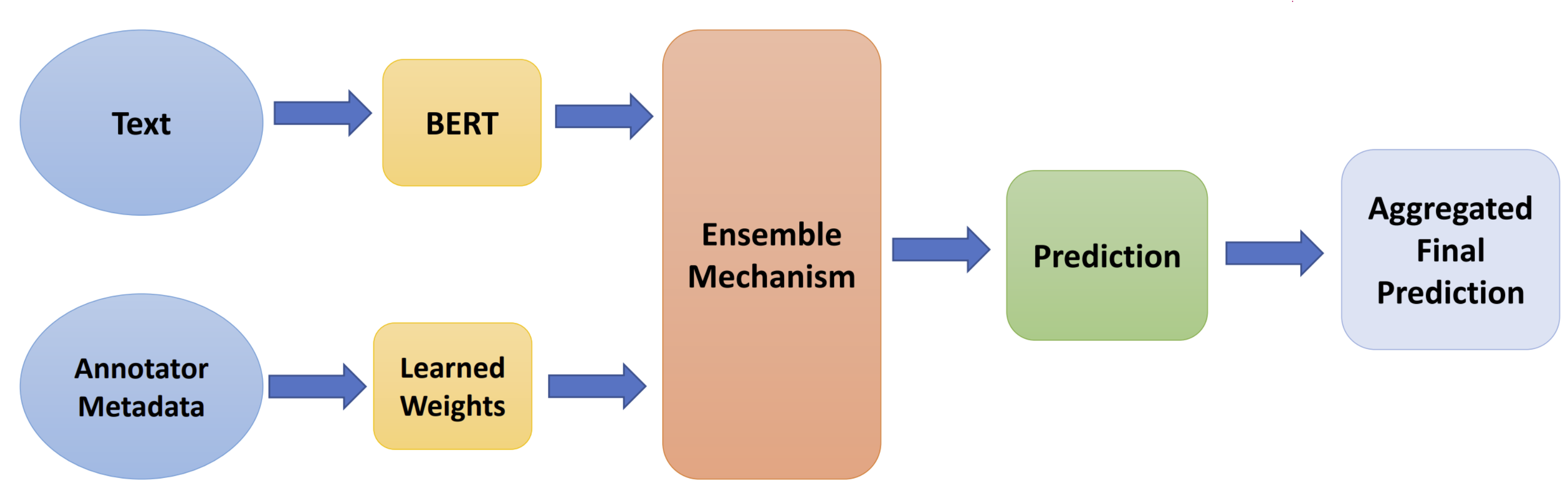
– Preserving the difference of opinion while labeling derogatory textual content can help us capture many important social phenomena like diversity of viewpoints. In this project, we aim to model subjectivity in the annotation of hate speech.
– Leveraged four datasets from SemEval-2023 Task 11 to explore and handle disagreement in the annotation process effectively. Performed training by fine-tuning a BERT model and compared a post-aggregation and disagreement-targeted learning approach.
– Demonstrated the effectiveness of individual annotator modeling and the importance of metadata association. Achieved a top ten spot in terms of cross-entropy score, and published in SemEval ‘23 conference.
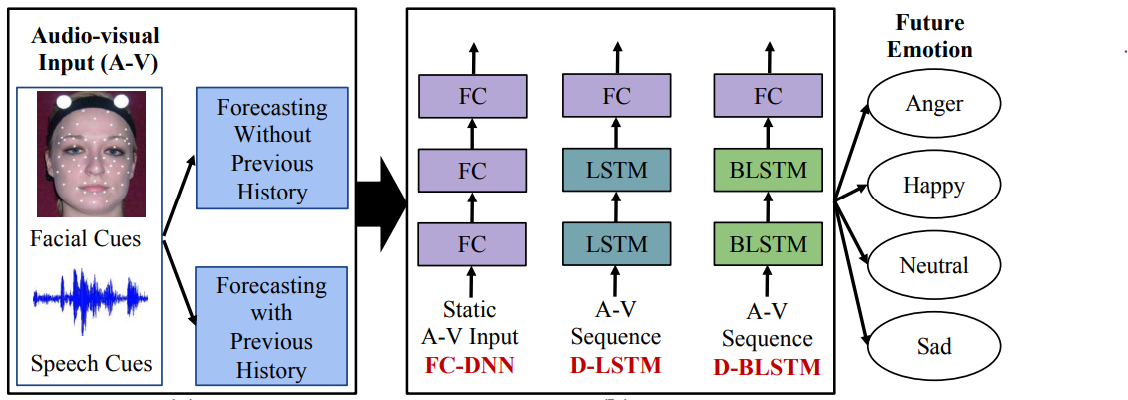
– Emotion forecasting is a novel task, aiming to predict a speaker's future emotional state based on their past and current audiovisual cues. Unlike traditional emotion recognition, it involves predicting emotions in advance and demands innovative problem formulations and modeling techniques.
– Explored two distinct forecasting windows: utterance forecasting and time forecasting. Assessed the impact of incorporating both past and current audiovisual cues in the emotion forecasting process. Compared three deep networks: FCDNN, D-BLSTM, D-LSTM.
– Demonstrated the superiority of dynamic models in the forecasting process by an improvement of 3% on average. Published the work in the prestigious FG ‘19 conference.